How to Reset a Home Circuit Breaker Troubleshoot Common Issues
In today's modern households, the home circuit breaker plays a crucial role in electrical safety and reliability. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures or malfunctions are responsible for an estimated 47,700 home fires each year, resulting in significant property damage and loss of life. A well-functioning home circuit breaker not only helps manage the distribution of electricity throughout the home but also acts as a safeguard against these dangerous incidents.
Understanding how to reset a home circuit breaker and troubleshoot common issues is essential for homeowners seeking to maintain a safe living environment. The U.S. Department of Energy reports that nearly 90% of all residential electrical fires could potentially be prevented with proper awareness and maintenance. As such, having a clear grasp of how a home circuit breaker operates, identifying its significance, and knowing how to effectively address common issues can empower homeowners to take proactive steps in safeguarding their homes.
With the right knowledge, resetting a home circuit breaker does not have to be a daunting task. This guide aims to provide homeowners with insightful information on effectively managing their circuit breakers, troubleshooting common issues, and ultimately ensuring their electrical systems operate safely and efficiently.
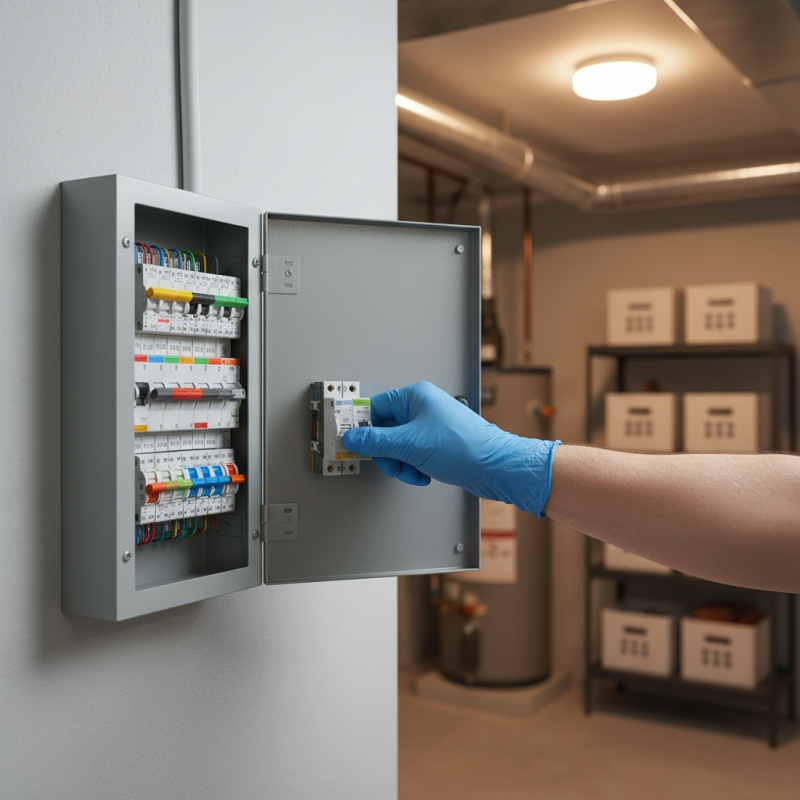

Understanding Home Circuit Breakers and Their Function
Home circuit breakers are essential safety devices designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. They act as a failsafe, automatically shutting off power when they detect an electrical fault. Understanding their function begins with recognizing their key role in a residential electrical system. Each breaker controls a specific circuit, ensuring that excessive current does not flow through the wiring, which could lead to potential hazards such as electrical fires.
When a circuit breaker trips, it interrupts the flow of electricity, allowing the circuit to cool down and preventing damage to electrical appliances and wiring. It is crucial for homeowners to familiarize themselves with their circuit breakers, including how to locate them and how to reset them if they trip. This knowledge not only enhances safety but makes troubleshooting electrical issues much more manageable. By understanding how breakers operate and the indicators of a tripped breaker, residents can effectively address common problems that may arise in their home’s electrical system.
Identifying Signs of a Tripped Circuit Breaker
Identifying signs of a tripped circuit breaker is essential for maintaining the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. A circuit breaker is designed to protect your home from electrical overloads and short circuits, and when it detects an issue, it automatically interrupts the current flow. One of the most common signs of a tripped circuit breaker is a sudden loss of power in specific areas of your home. If you find that certain lights go out or appliances stop functioning without any apparent reason, it’s likely that a circuit breaker has tripped. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures or malfunctions are responsible for an estimated 47,700 reported home fires every year in the United States, highlighting the critical nature of recognizing these indicators.
Another common sign is the presence of a flickering or dimming light, which can indicate that the circuit is overloaded. In fact, the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission reports that improperly functioning electrical systems contribute to “thousands of injuries” annually. If you notice signs of overheating, such as warm or discolored outlets and switch plates, it’s vital to check your circuit breakers. Most modern breakers are equipped with a reset mechanism that can easily indicate their status—if the lever is in the ‘off’ position, it is a tell-tale sign that it has tripped. Awareness of these indicators can not only save you time and money but also prevent potential hazards due to electrical failures.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reset a Circuit Breaker
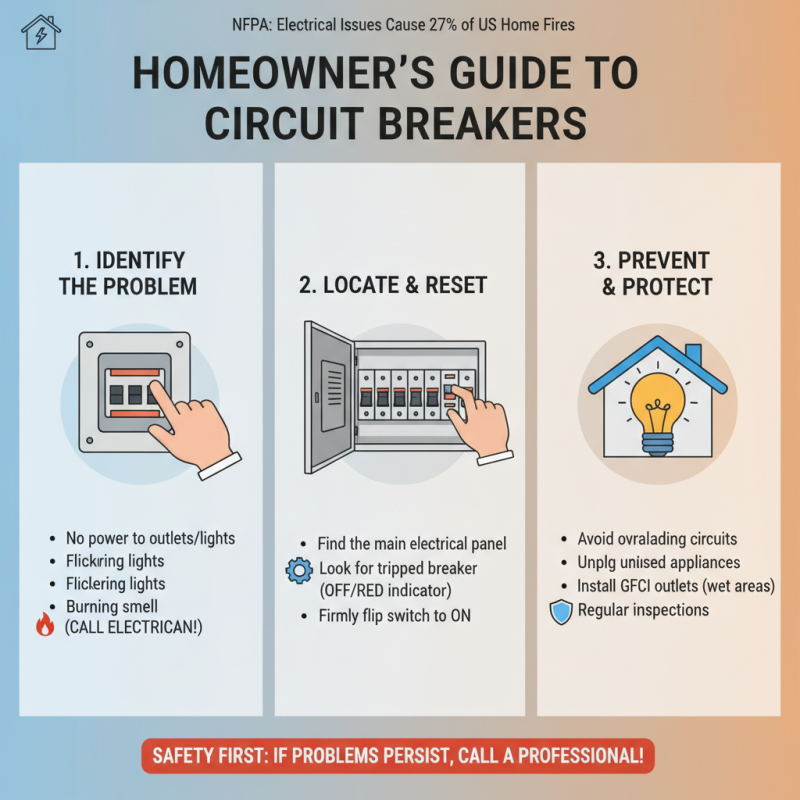
Resetting a home circuit breaker is an essential skill for any homeowner, especially when facing common electrical issues. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical malfunctions are among the leading causes of residential fires, accounting for 27% of reported fires in the U.S. Understanding how to troubleshoot and reset a circuit breaker can significantly reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
To reset a circuit breaker, first, identify the tripped breaker in your panel. A tripped breaker typically sits in the "off" position or may show a red indicator. Flip the breaker fully to the "off" position before returning it to "on." This simple action can resolve issues caused by overloaded circuits or short circuits. The Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) emphasizes the importance of ensuring that your electrical system is up to code and recommends regular inspections as proactive measures to avoid unexpected power outages or failures.
While most circuit breaker resets are straightforward, persistent issues may require further investigation. If a breaker trips frequently, it could indicate an overloaded circuit or a fault in the wiring. In fact, a report by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission indicates that more than 50,000 home electrical fires occur annually due to these unresolved issues. Ensuring that you know how to troubleshoot effectively can save both time and enhance safety within your household electrical system.
Common Issues After Resetting and Their Solutions
After resetting a home circuit breaker, it’s common to encounter a few issues that could affect the proper functioning of your electrical systems. One frequent problem is that the breaker trips again shortly after being reset. This could indicate an overloaded circuit, which happens when too many devices are drawing power from a single breaker. To resolve this, it’s advisable to unplug some devices and redistribute the load to other circuits. If the problem persists, there may be a short circuit or a ground fault, necessitating further investigation, perhaps with the help of a qualified electrician.
Another issue that can arise is flickering lights, which often signals an instability in the electrical circuit. This can occur if the connections within the outlet or at the breaker are loose. Checking and tightening any loose connections can sometimes eliminate the flickering. If this does not resolve the issue, the problem might lie within the light fixture or the bulb itself, so it would be prudent to inspect those components as well. Taking these steps can help ensure your home's electrical system remains safe and efficient after a reset.
Common Issues After Resetting a Home Circuit Breaker
Preventive Measures to Avoid Future Breaker Trips
Preventive measures are crucial in ensuring the long-term reliability of your home's electrical system and avoiding frequent circuit breaker trips. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures are the second leading cause of home fires, accounting for approximately 13% of all residential fire incidents. One key strategy to mitigate these risks is regular inspection and maintenance of electrical systems. Homeowners should consider having a qualified electrician conduct an annual review of their wiring and circuit breakers to identify signs of wear or potential overloads.
In addition, understanding power demands is vital to preventing overloads that can trip circuit breakers. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) reports that the average American household consumes roughly 877 kWh per month, leading to increased strain on home circuits, especially in older homes. To manage this effectively, it's wise to distribute high-energy appliances across different circuits and avoid using multiple high-wattage devices simultaneously on a single breaker. Implementing surge protectors and ensuring that outlets are not overloaded can also contribute to a safer electrical environment, reducing the likelihood of unexpected trips.
Furthermore, practicing mindful electrical use can significantly lower the chances of breaker trips. Utilizing smart plugs or energy monitoring devices can provide insights into energy consumption and alert homeowners to potential issues before they arise. By adopting these preventive measures, homeowners can greatly enhance the safety of their electrical systems and minimize the disruptions caused by circuit breaker trips.
How to Reset a Home Circuit Breaker Troubleshoot Common Issues - Preventive Measures to Avoid Future Breaker Trips
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breaker Trips Frequently | Overloaded Circuit | Redistribute load or reduce connected devices | Regularly check and manage device usage |
| Breaker Won't Reset | Short Circuit | Find and repair the short before resetting | Inspect wires and connections regularly |
| Breaker Feels Warm | Loose Connections | Tighten connections safely | Schedule periodic maintenance |
| Blinking Lights | Voltage Fluctuations | Consider a voltage stabilizer | Monitor electrical load and connections |
| Power Outage | External Factors | Contact utility provider | Prepare an emergency kit |
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Air Circuit Breakers: Best Options for Your Electrical Needs
-

Understanding Power Circuit Breakers: Key Features, Benefits, and Maintenance Tips for Home Safety
-
10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Miniature Circuit Breaker for Your Projects
-

7 Facts You Didn't Know About ACB Breakers: The Best Choices for Your Electrical Needs
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Air Circuit Breaker for Your Electrical Systems
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Vacuum Circuit Breakers for Your Electrical System