What is DC to DC Conversion and How Does it Work?
DC to DC conversion is a crucial aspect of modern electronics. This process allows devices to efficiently manage power requirements. As industry expert John Smith states, “DC to DC conversion is vital for optimal device performance.” His insight emphasizes the importance of this technology in our daily lives.
In essence, DC to DC converters adjust voltage levels for specific applications. This balance is key for devices such as smartphones and electric vehicles. However, many overlook the complexities involved. The design and efficiency of these converters can significantly impact performance and lifespan. It's not just about the technology; it's about how we utilize it.
Moreover, understanding DC to DC conversion brings challenges. Issues like heat dissipation and power loss are common in the industry. While advancements have been made, there's still room for improvement. Reflecting on these hurdles can drive innovation. Recognizing our limitations is the first step to overcoming them.

What is DC to DC Conversion?
DC to DC conversion is a critical process in electronics. It involves transforming direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. This is essential in various applications. For instance, it powers smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, providing versatility in energy needs.
The need for reliable DC to DC converters is increasing. According to a recent market report, this sector is expected to reach $30 billion by 2026. Many applications require different voltage levels. Thus, a well-designed converter ensures efficient energy management. A poorly designed converter can lead to energy losses, impacting performance and lifespan.
Ensuring compatibility is challenging. Different devices have varying voltage and current requirements. It’s essential to select converters that match these needs precisely. Research indicates that improper conversion can cause failures in 30% of electronic devices. This highlights the importance of investment in high-quality conversion technologies. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing reliable electronic systems.
Principles of DC to DC Conversion
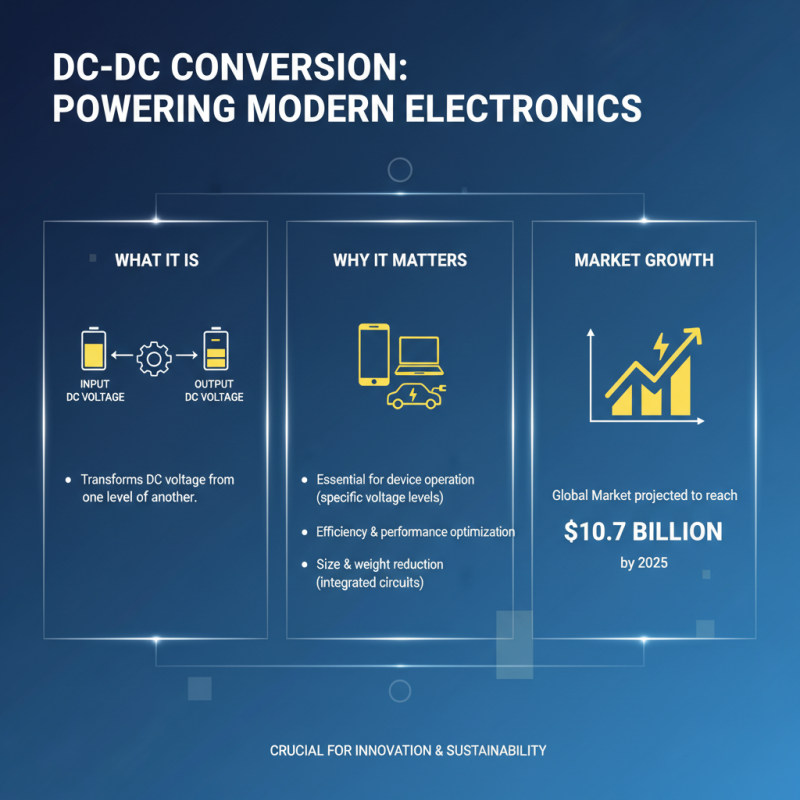
DC to DC conversion plays a crucial role in modern electronics. It transforms one DC voltage level to another. This process is vital for devices that need specific voltage levels for optimal operation. In fact, the global DC-DC converter market is projected to reach $10.7 billion by 2025, highlighting its growing significance.
The principles of DC to DC conversion hinge on two main techniques: buck and boost conversion. Buck converters reduce voltage, making them ideal for applications like battery management. Conversely, boost converters increase voltage, which proves useful in solar applications. The efficiency of these converters can reach up to 95%. However, challenges remain. Ripple voltage can affect device performance.
Moreover, thermal management is often overlooked. Heat can reduce efficiency and lifespan. Ensuring proper cooling is essential. Inadequate design can lead to significant losses. Thus, while DC to DC conversion is effective, it requires careful planning. The process includes trade-offs between efficiency and complexity. The need for compact designs further complicates matters. Understanding these principles leads to better designs and improved reliability.
Common Types of DC to DC Converters
DC to DC converters are essential devices in electronics. They convert one DC voltage level to another. This process is crucial for many applications such as powering mobile devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. There are several common types of DC to DC converters.
One popular type is the buck converter. It steps down the voltage while increasing the current. This design is efficient and can be found in battery chargers. Another common type is the boost converter. It increases voltage while reducing current. Boost converters are often used in applications requiring high voltages from low voltage batteries.
Lastly, there's the buck-boost converter. This versatile converter can either step up or step down the voltage. Its flexibility makes it valuable in various situations, especially when working with fluctuating input levels. However, the complexity of these circuits can lead to design challenges and inefficiencies. Understanding these types is vital in creating reliable electronic systems. Each converter has its advantages and trade-offs, warranting careful consideration in design.
Common Types of DC to DC Converters
| Type of Converter | Input Voltage Range | Output Voltage Range | Efficiency (%) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buck Converter | 3V - 30V | 1.2V - 15V | 85 - 95 | Power Supplies, Battery Charging |
| Boost Converter | 1.5V - 20V | 3V - 30V | 80 - 90 | Portable Devices, LED Drivers |
| Buck-Boost Converter | 2.5V - 15V | 1.5V - 20V | 80 - 90 | Battery Management, Solar Applications |
| Cuk Converter | 3V - 20V | 1.5V - 30V | 85 - 90 | Power Supplies, Low-Voltage Applications |
| SEPIC Converter | 3V - 20V | 1V - 30V | 85 - 95 | Communication Equipment, Automotive |
Applications of DC to DC Conversion
DC to DC conversion plays a critical role in modern electronics. It provides the ability to change one DC voltage level to another. This process is essential for powering various devices efficiently. Many applications leverage this technology for improved performance.
One significant area is renewable energy systems. Solar panels produce DC electricity, which needs conversion to power homes. The conversion ensures proper voltage levels for different appliances. Another crucial application is in portable electronics. Devices like smartphones require various voltage levels for their components. Efficient DC to DC converters make this possible, extending battery life and enhancing functionality.
In automotive applications, DC to DC conversion supports electric vehicles. These vehicles require multiple voltage levels for different systems. Proper conversion enhances performance and safety. Despite the technology's advantages, challenges remain. Designers often face efficiency issues. Balancing size and heat dissipation can be difficult. These factors require continuous innovation and improvement.
Key Advantages and Challenges in DC to DC Conversion
DC to DC conversion offers significant advantages, particularly in efficiency and versatility. According to a recent industry report, DC-DC converters can achieve efficiency levels exceeding 90%. This efficiency is vital in applications like renewable energy systems and electric vehicles. With energy costs rising, optimizing power management is essential. Lower energy loss translates to cost savings and reduces heat generation, prolonging equipment life.
However, DC to DC conversion presents several challenges. The circuitry can be complex. In specific applications, design considerations become crucial. High-frequency switching can introduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), which may affect nearby components. Furthermore, the compatibility of different voltage levels may lead to integration issues.
Industry reports also indicate that the demand for more compact designs leads to heat management challenges. As devices become smaller, managing heat dissipation grows more difficult. This can affect code reliability and overall system performance. Balancing efficiency with thermal management remains an area needing attention. While the benefits of DC to DC conversion are clear, addressing these challenges is vital for future advancements.
DC to DC Conversion: Efficiency and Application Areas
Related Posts
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best DC to DC Converter for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Importance of MCCB Breakers in Modern Electrical Systems
-

Understanding Power Circuit Breakers: Key Features, Benefits, and Maintenance Tips for Home Safety
-

Why Surge Protection is Essential for Your Home and Business Safety
-

Understanding the Challenges of Miniature Circuit Breakers in Modern Electrical Systems
-

Top 10 Surge Protective Devices for Home and Office Use to Ensure Your Electronics Safety