How to Choose the Right Air Circuit Breaker for Your Electrical System
When selecting the appropriate air circuit breaker for an electrical system, it is crucial to understand the unique requirements and challenges posed by the system's design and operational demands. According to a recent report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the demand for high-performance air circuit breakers is projected to increase by 5% annually through 2025, driven by advancements in electrical systems and infrastructure. These devices play a key role in protecting equipment and ensuring safety in various applications, from industrial sectors to commercial buildings.
Expert insights further illuminate the importance of this selection process. James L. Harper, a veteran in power systems engineering, emphasizes, "Choosing the right air circuit breaker is not just about technical specifications; it's about understanding the environment and load requirements that dictate performance." His statement highlights the necessity for a tailored approach, considering factors such as thermal and magnetic protection, operational reliability, and maintainability. As electrical systems evolve, selecting the right air circuit breaker becomes increasingly critical for achieving both efficiency and safety in modern installations.
Understanding the Basics of Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) in Electrical Systems
Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) play a crucial role in the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. An ACB is designed to provide overcurrent protection and is particularly effective in high-voltage applications. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, the demand for reliable ACBs is on the rise, driven by the growing need for energy-efficient solutions in commercial and industrial sectors. ACBs serve not only to prevent damage from overloads and short circuits but also contribute to the overall stability of electrical networks by ensuring a consistent power supply.
Understanding the operational principles of ACBs is key to choosing the right one for your system. These devices utilize air as an insulator and a medium to quench the arc during the interruption process. This feature allows for effective thermal management, making ACBs capable of handling high current operations—often rated from 800A to 10,000A or more. Furthermore, data from the Global Circuit Breaker Market Report indicates that advancements in digital technologies are enhancing ACB functionalities, including remote monitoring capabilities and advanced protective features. By selecting appropriately rated ACBs, users can ensure compliance with industry standards while safeguarding their electrical systems against potential hazards.
How to Choose the Right Air Circuit Breaker for Your Electrical System
| Parameter | Description | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|
| Current Rating | The maximum current the ACB can carry without tripping. | 100A to 4000A |
| Short-Circuit Protection | Ability to protect the circuit during short-circuit conditions. | Rating 6kA to 100kA |
| Tripping Characteristics | The response time of the ACB when an overload occurs. | Inverse time, Standard or Selective |
| Number of Poles | Number of electrical connections for carrying current. | 2P, 3P, 4P |
| Operating Mechanism | Type of mechanism that operates the ACB. | Manual or Automatic |
| Environmental Rating | Protection against dust and moisture. | IP20, IP54, IP65 |
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting ACB Ratings for Your System
When selecting an Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) for your electrical system, it is essential to consider several key factors that ensure optimal performance and reliability. One critical aspect is the rated current of your ACB, which should be matched to the load requirements of your system. This involves calculating the total load and ensuring that the ACB can handle the expected maximum current without tripping unnecessarily. Additionally, understanding the fault current of your system can help in selecting an ACB with adequate short-circuit protection.
Another important factor to contemplate is the operational environment where the ACB will be installed. Conditions such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to dust or corrosive materials can affect the performance of the breaker. ACBs with appropriate environmental ratings can ensure longevity and reliability in adverse conditions.
**Tips**: Always consult with an electrical engineer to analyze system input and consider future expansion needs. Moreover, ensure to check the ACB’s interruption capacity to guarantee it can effectively manage fault currents, protecting your system from damage. Lastly, evaluating the maintenance and accessibility of the circuit breaker installation can lead to easier troubleshooting and servicing in the future.
Analyzing Short-Circuit Protection and Its Importance in ACB Selection
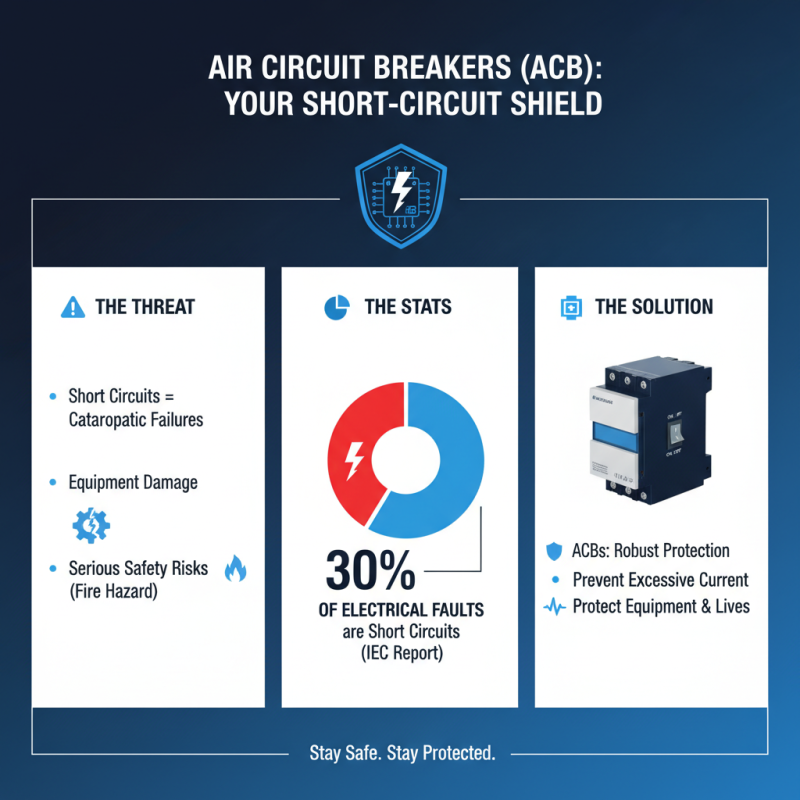
When selecting an air circuit breaker (ACB) for an electrical system, understanding short-circuit protection is crucial. Short circuits can lead to catastrophic failures in electrical systems, causing damage not only to the equipment but also posing serious safety risks. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), approximately 30% of electrical faults originate from short circuits. This underscores the importance of having robust protection mechanisms like ACBs to prevent excessive current from causing fire hazards and equipment damage.
The selection process for an ACB must focus on its short-circuit rating, which is defined as the maximum current the breaker can safely interrupt without sustaining damage. The IEEE standards recommend that this rating should exceed the maximum short-circuit current potential at the installation point by a safety margin of at least 25%. Additionally, analyzing the system's configuration and the operational environment is essential, as factors such as ambient temperature and humidity can affect the performance of ACBs. By conducting thorough calculations and considering these variables, engineers can ensure that the ACB will perform effectively when faced with a short-circuit situation, thus safeguarding the entire electrical system.
Comparing ACB Types: Double-Function vs. Combined Function Breakers
When selecting an air circuit breaker (ACB) for your electrical system, understanding the different types available is crucial. Among these, double-function and combined function breakers stand out for their unique features and applications. Double-function breakers are designed to provide dual protection by integrating both overcurrent and earth fault protection in a single unit. This efficiency not only saves space in the electrical panel but also simplifies maintenance and reduces installation costs. They are ideal for systems where space is at a premium or where the load conditions are relatively stable.
On the other hand, combined function breakers offer additional versatility by incorporating more protective features such as short circuit protection alongside the functions of traditional double-function breakers. This makes them suitable for applications with unpredictable load changes, where more comprehensive protection mechanisms are necessary. These breakers are often used in industrial settings where electrical faults can lead to severe consequences. Understanding the differences between these two types of ACBs can help in making a better-informed decision tailored to the specific needs of your electrical installation, ensuring both safety and reliability in power distribution.
Evaluating Environmental and Installation Conditions for ACB Performance
When selecting the right air circuit breaker (ACB) for your electrical system, it is essential to evaluate the environmental and installation conditions that can significantly impact ACB performance. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and dust levels in the installation site play crucial roles. For instance, ACBs function optimally within a specific temperature range; extreme heat or cold can affect their reliability and responsiveness. High humidity can lead to corrosion and short-circuiting, while excessive dust may impede the mechanical operation of the breaker. Assessing these environmental aspects ensures that the chosen ACB is suited for the conditions it will face, enhancing its lifespan and efficiency.
Moreover, the installation conditions, including the available space, mounting configuration, and proximity to other electrical equipment, should also be taken into account. For example, ensuring adequate cooling and ventilation around the ACB can prevent overheating and mechanical failures. Furthermore, considering the breaker’s orientation and the electrical load it will serve is vital for optimal functionality. An understanding of these installation prerequisites can guide users in selecting an ACB that not only meets regulatory standards but also provides reliable protection for their electrical system. By thoroughly evaluating both environmental and installation conditions, users can make informed decisions that enhance the safety and efficiency of their electrical systems.
Air Circuit Breaker Performance Evaluation
This chart illustrates the performance of Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) under various environmental conditions, focusing on temperature, humidity, and installation environments. The data represents typical performance metrics relevant to circuit breakers.
Related Posts
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Electric Breaker for Your Needs
-

What is the Function of a DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
-

Common Issues with Electric Breakers: A Global Purchasing Insight
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Surge Protection Circuit Breaker for Your Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Electric Breaker for Your Home and Business Needs
-
Understanding Power Circuit Breakers: The Key to Safe Electrical Systems