How to Choose the Right Surge Protective Device for Your Needs?
Selecting the right surge protective device (SPD) can seem daunting. With various options available, how do you choose? Renowned industry expert, Dr. Jane Smith, emphasizes, “A surge protective device is essential to safeguard your valuable electronics.” This statement highlights the importance of making an informed choice.
Understanding your specific needs is crucial. Different devices cater to different environments. For instance, residential spaces typically require smaller, more compact SPDs. In contrast, commercial applications might demand more robust protection. Each context has unique vulnerabilities, impacting your decision significantly.
When evaluating options, pay attention to key features. Look for devices with reliable ratings. Consider the clamping voltage and response time. These details matter, as they determine how effectively the SPD will work. Remember, an informed choice today can prevent costly damage tomorrow.

Understanding Surge Protective Devices: An Overview
Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) are essential for protecting sensitive electronics. These devices absorb excess voltage from surges, such as those caused by lightning. A recent industry report states that nearly 60% of power quality problems are due to various electrical disturbances.
Understanding the types of SPDs is crucial. There are three major classes: Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3. Type 1 devices are installed at the service entrance. They offer robust protection against external surges. Type 2 devices protect the internal wiring, while Type 3 devices are terminal devices that safeguard individual equipment. A well-rounded approach often includes a combination of these types to ensure comprehensive protection.
Many users underestimate the need for regular testing and replacement of SPDs. According to studies, around 30% of installed SPDs are ineffective due to aging or improper installation. This oversight can lead to significant equipment damage over time. Investing in quality surge protection devices, while also maintaining them, is key to safeguarding your valuable electronics.
How to Choose the Right Surge Protective Device for Your Needs?
| Type of Surge Protective Device | Voltage Rating | Max Surge Current (kA) | Response Time (ns) | Installation Location | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | 120/240V | 100 | 25 | Main electrical panel | Residential applications |
| Type 2 | 120/240V | 50 | 35 | Subpanel | Commercial applications |
| Type 3 | 120V | 30 | 50 | Point of use (plugs) | Sensitive electronic devices |
| Type 4 | 480V | 200 | 10 | Industrial equipment | Heavy machinery |
Identifying Your Power Needs and Potential Risks
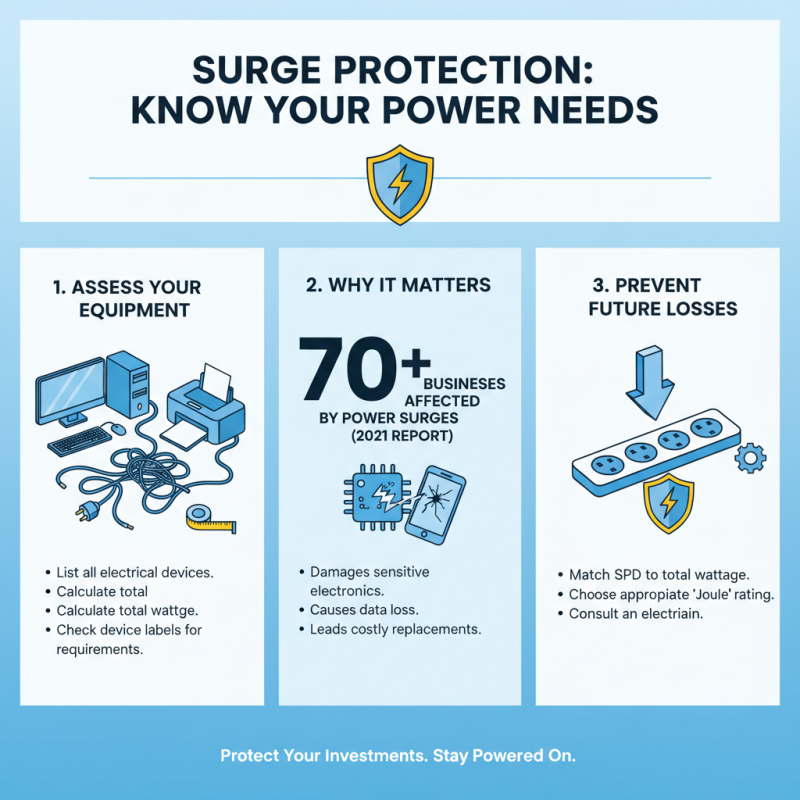
Identifying your power needs is crucial when selecting a surge protective device (SPD). Begin by assessing your electrical equipment. Consider the total wattage your devices require. According to a 2021 industry report, over 70% of businesses experience power surges. These surges can damage sensitive electronics. Knowing your equipment's power demands helps prevent future losses.
Next, evaluate your environment. Are you located in an area prone to thunderstorms or unstable power supply? Statistics show that regions with frequent lightning strikes face 20% more electrical disturbances. Installing an SPD that can withstand these risks protects your investments. It's also essential to account for the age of your wiring systems. Older systems may not handle surges well, requiring more robust protection.
While it’s easy to focus solely on high-end products, a balance between cost and effectiveness is vital. Many basic SPDs offer adequate safety for domestic use. However, businesses need a higher level of protection. If unsure, consulting a professional can shed light on your specific risks. Don’t overlook the possibility of having insufficient coverage. Regularly reviewing your power needs can prevent unexpected expenses in the future. Consider the unique challenges your setup may face.
Evaluating Different Types of Surge Protective Devices
When evaluating surge protective devices (SPDs), it’s crucial to understand the different types available. There are primarily three categories: Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3. Type 1 devices are installed at the service entrance. They are best for whole-home protection. Type 2 devices are typically used in subpanels. They offer a second layer of defense. Type 3 devices are point-of-use protectors. They are meant for sensitive electronics.
Each type has unique characteristics. Type 1 devices can handle large surges but may require professional installation. Type 2 devices offer flexibility and can be installed in various locations. Type 3 devices are compact and easy to install. However, they may not protect against all surge levels. Assess your specific needs and the common voltage levels in your area. Understanding what you need can guide you in making a sound decision.
The right SPD can safeguard your equipment, but choosing can be tricky. Some users don’t fully understand their power needs. This can lead to under or over protection. Evaluate your appliances' sensitivity to surges. Reflect on past surge events if applicable. A knowledgeable decision can help in preventing costly damages.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Device
When choosing a surge protective device (SPD), several key features should be considered. One crucial factor is the device's voltage rating. According to industry reports, improper voltage ratings can lead to device failure. A spike in voltage can exceed the SPD's limits, compromising its effectiveness. Selecting a device that matches the voltage levels of your equipment is vital.
Another important feature is the surge protection capacity, often measured in joules. A report from the Electrical Safety Foundation indicates that higher joule ratings typically offer more protection. Devices with lower ratings may not withstand severe surges. Notably, many manufacturers suggest looking for SPDs with at least 4000 joules for residential use. This baseline can help you avoid costly equipment damage.
Response time is also vital. Some SPDs react within nanoseconds, while others take longer. A slower response can result in equipment damage during a surge. Industry studies show that devices with quicker response times offer better protection. However, many users overlook this feature. Careful consideration of these specifications is necessary when making a choice.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Optimal Protection
When it comes to surge protective devices, installation is key. Proper placement can significantly enhance their effectiveness. Install devices near the main electrical panel. This helps guard your entire system against surges. Ensure connections are tight and secure. Loose connections can lead to issues and reduce protection levels.
Maintenance also plays a vital role. Regularly inspect your surge protectors for any signs of wear or damage. Look for burnt smells or discolored parts. These could indicate a malfunction. If a device is damaged, replace it promptly. Ignoring this could leave your equipment vulnerable. It’s essential to understand that some devices have indicators showing they're still functioning. Pay attention to these signals.
Remember to adjust your approach based on your specific needs. Not all environments are the same. A device suitable for a home might not work well in an industrial setting. Reflect on your power demands. This ensures the protection you choose aligns with your environment and usage. Adapting your strategy may require some trial and error.
Surge Protective Device Ratings and Features
This chart illustrates essential features of surge protective devices, including voltage rating, energy rating, response time, and maximum surge current capacity. When selecting the right device for your needs, consider these factors to ensure comprehensive protection for your electrical systems.
Related Posts
-

2026 Best Surge Protective Device Choices for Home and Office Safety?
-

Top 10 Surge Protective Devices for Home and Office Use to Ensure Your Electronics Safety
-

How to Choose the Right DC Surge Protection Device for Your Needs
-

2026 How to Choose the Right Surge Protective Device for Your Home?
-

Essential Tips for Effective Surge Protection at Home
-
Top Air Circuit Breaker Protection Relay Features You Need to Know